Hair loss

Hair Loss Explained: Causes, Prevention Tips & Treatment Options
Hair loss, also known as alopecia, is a common condition that can affect individuals of all ages and genders. It may be temporary or permanent and can occur on its own or as a symptom of an underlying health issue. While not physically harmful in most cases, hair loss often has a significant emotional impact, especially among women, and can affect personal confidence, relationships, and mental health.
Thankfully, there are several effective ways to diagnose, prevent, and treat hair loss—once the root cause is identified. This is particularly important for women, as the causes and patterns of female hair loss can be harder to detect and treat accurately.
Recognising the Symptoms of Hair Loss
Hair loss itself is a symptom, but identifying the pattern and associated changes can help in understanding the underlying cause. Here are some of the most common signs:
- Diffuse thinning— Gradual reduction in volume across the entire scalp, often associated with female pattern hair loss or telogen effluvium
- Receding hairline— Common in male pattern baldness and traction alopecia, especially at the temples
- Bald spot on the crown— Frequently linked to androgenetic alopecia in men
- Widening parting— A typical early sign in women with female pattern baldness
- Circular bald patches— Small, coin-sized patches of hair loss could indicate alopecia areata
- Complete scalp hair loss— Known as alopecia totalis, or could be due to chemotherapy treatment
- Full body hair loss — A rare condition called alopecia universalis, where hair is lost from the entire body

Other signs to look for:
- Scaling and flaking— may suggest scalp conditions such as psoriasis, seborrheic dermatitis, or ringworm
- Changes in hair texture— hair that becomes unusually dry, brittle, or breaks easily may be a sign of damage or poor haircare
- Feeling anxious or worried— stress-induced hair loss, including telogen effluvium, is often linked to emotional or physical strain

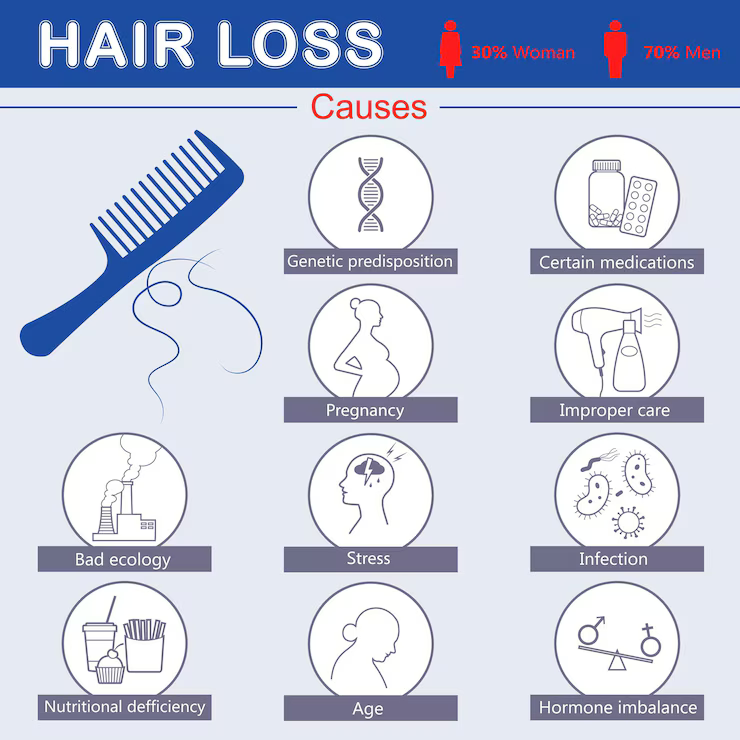
Common Causes of Hair Loss
Several factors can trigger or contribute to hair loss. Understanding these can help you determine the right treatment plan:
- Normal shedding— It’s completely normal to shed between 50–100 hairs a day. Hair fall beyond this amount may require further investigation
- Genetic factors and hormones— The most common cause of permanent hair loss is androgenetic alopecia, which is influenced by genetics and hormonal imbalances—especially around menopause, pregnancy, or puberty
- Autoimmune diseases— In conditions like alopecia areata, the immune system attacks the hair follicles, causing patchy or widespread hair loss
- Emotional stress or trauma— High stress can shock the body into telogen effluvium, pushing hair into the shedding phase earlier than normal
- Medications— Drugs such as chemotherapy agents, antidepressants, or vitamin A supplements can contribute to hair thinning or loss
- Nutritional deficiencies— A lack of iron, protein, zinc, or vitamin D can starve hair follicles of nutrients, slowing or stopping growth
- Styling and chemical damage— Overuse of heat tools, bleach, or tight hairstyles can weaken the hair shaft and create the illusion of hair thinning
What Should You Do If You Notice Hair Loss?
If you’re noticing more hair fall than usual, or changes in hair density or texture, the first step is to consult a GP or dermatologist. Once serious conditions are ruled out, a trichologist—a specialist in scalp and hair health—can guide you through diagnosis and treatment options tailored to your needs.
Expert hair transplant care for natural results
Restore your hair with advanced transplantation techniques and consultations with our specialists.
Hair Loss Treatments
A variety of proven treatments are available for individuals experiencing hair loss. The most effective option for each person depends on the cause, extent, and pattern of their condition. Here are some popular options:
- Hair Transplant Surgery— Considered the most effective solution for permanent hair loss, this procedure involves transplanting healthy hair follicles from a donor area to thinning or bald patches.
- Finasteride — A daily oral medication used to treat male pattern baldness by lowering DHT levels, helping to prevent further loss and support regrowth.
- Minoxidil — Available as a topical solution or oral tablet, Minoxidil boosts blood circulation in the scalp and is effective for various types of alopecia.
- Dutasteride — A more potent alternative to Finasteride, often used in advanced cases of male pattern hair loss to block DHT more aggressively.
- Corticosteroids — Topical creams or injections that reduce inflammation and are particularly effective for autoimmune-related hair loss like alopecia areata.
- JAK Inhibitors (e.g., Ritlecitinib, Olumiant)— These medications suppress immune response and are showing promising results for treating moderate to severe alopecia areata.
- Low-Level Laser Therapy (LLLT)— A non-invasive laser treatment that stimulates the scalp at the cellular level, supporting healthier follicles and new growth.
Hair Loss Prevention
Certain types of hair loss are preventable—especially when linked to stress, nutrition, or poor styling practices. Below are practical ways to help maintain healthy hair:
- Eat a balanced, nutrient-rich diet with enough protein, vitamins, and iron to fuel hair growth.
- Avoid excessive heat styling and harsh chemicals like bleach and permanent dyes that weaken hair.
- Keep hairstyles loose to avoid stress on the scalp (avoid tight buns, braids, or extensions).
- Quit smoking and limit alcohol —both can restrict blood flow to the scalp and follicles.
- Use stress-management techniques like yoga, mindfulness, or therapy to avoid hair fall linked to anxiety.
- Consult your GP or a trichologist to rule out underlying causes like thyroid issues or nutrient deficiencies.
